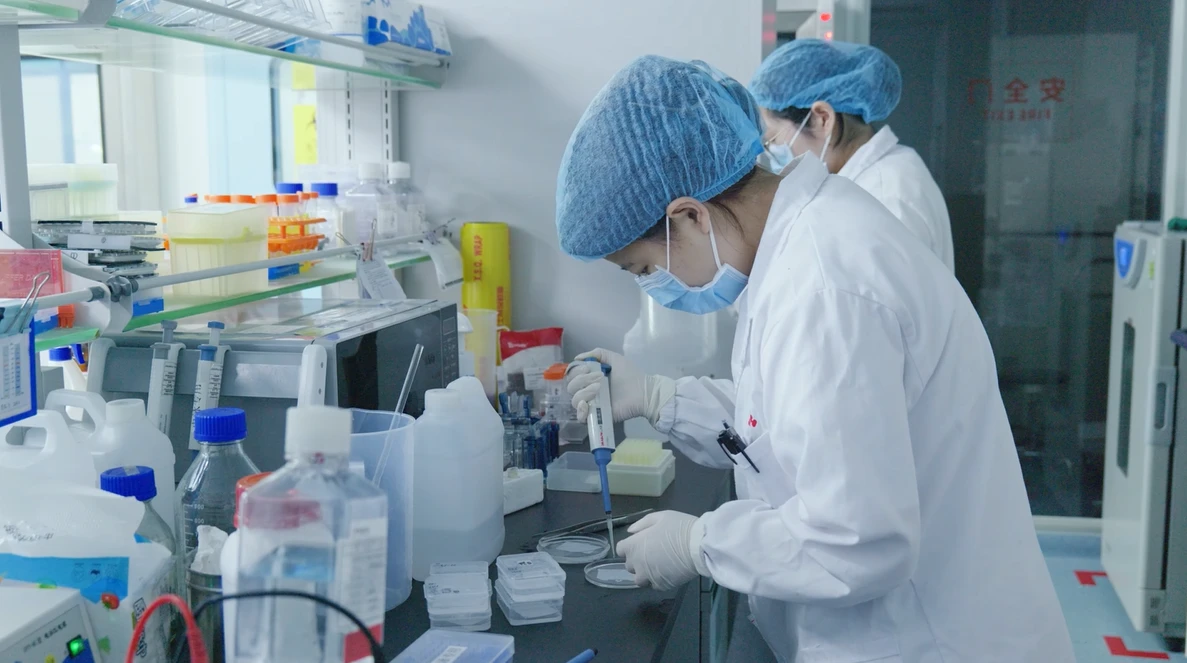
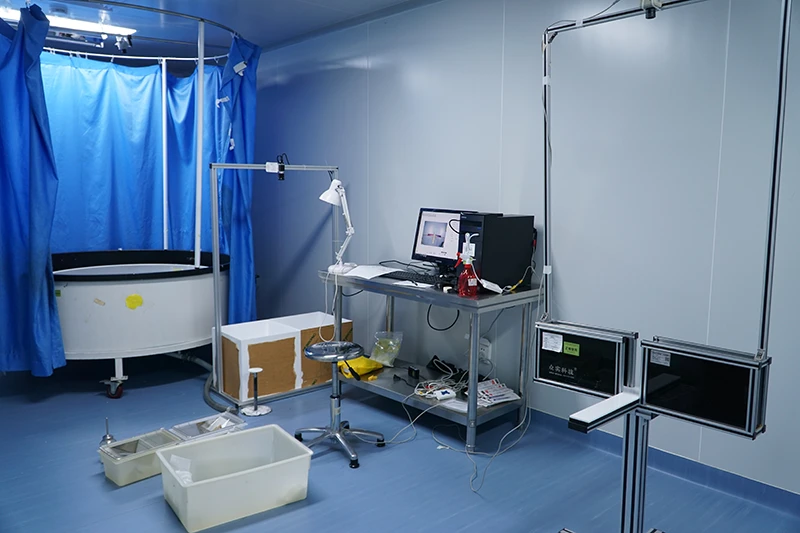
Animal models are a crucial part of medical device testing, providing essential data that supports the evaluation of medical devices for safety, efficacy, and long-term performance. While bench testing and computer simulations offer valuable insights, they cannot replicate the complexity of biological systems. Animal models are critical for assessing how a device interacts with living tissues and how it performs in real-world biological conditions.
This article explains how animal models support device testing, how they meet medical device regulations, and why they are essential for ensuring safety and performance in the long term.
Why Animal Testing Remains Essential for Device Testing
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and NMPA require robust scientific data before a device can be approved for human trials. Animal models provide the long-term safety data that is needed to move forward in the clinical development process. They help developers understand:
- How the device interacts with biological systems over time
- Whether the device causes systemic toxicity or other adverse effects
- How the device performs in a real biological environment
- The long-term effects of implantation, degradation, and integration
For medical device manufacturers, using animal models to support evaluation of medical devices is vital to reducing risks and improving the safety and efficacy of new devices.
How Animal Models Support Device Testing
1. Proving Biocompatibility: ISO 10993 and In Vivo Testing
The ISO 10993 standard is critical for assessing the biocompatibility of medical devices. While some tests, like cytotoxicity, can be done in vitro, in vivo studies are needed to understand how tissues respond to an implanted device over time. Animal testing helps assess:
- Local tissue responses (e.g., inflammation, irritation, or fibrosis)
- Systemic toxicity and the potential for adverse immune reactions
- Bone integration for orthopedic and dental implants
- The long-term healing process for bioresorbable materials
For example, sheep are often used in bone integration studies to test how well spinal implants bond with bone. These in vivo studies provide essential data for both regulatory submissions and device design.
2. Validating Device Function and Long-Term Performance
In addition to assessing biocompatibility and safety, animal models are indispensable for evaluating the function, performance, and long-term outcomes of medical devices. Testing in animals allows researchers to observe how devices behave in complex biological systems and under conditions that cannot be replicated through computational models or in vitro studies.
2.1 Cardiovascular Devices
For cardiovascular devices, pigs and sheep are often used due to their anatomical and physiological similarities to humans. These models are crucial for testing:
- Blood flow dynamics and device interaction with blood vessels
- Long-term device performance, including potential complications such as thrombosis, restenosis, or inflammation
- Biocompatibility of stents, pacemakers, and vascular grafts
These studies ensure the device's safety and performance over the long term, critical for devices designed for chronic or lifetime use.
2.2 Orthopedic and Dental Implants
For orthopedic implants and dental implants, species such as sheep, pigs, and dogs are commonly used to study:
- The mechanical properties of implants under weight-bearing conditions
- Bone healing, integration, and remodeling around implants
- Long-term stability of implants, especially for load-bearing devices
These models are vital for ensuring that orthopedic and dental implants not only integrate properly with bone but also withstand the stresses of daily use over an extended period.
2.3 Neurostimulation and Neuroprosthetics
Neurostimulation devices, such as deep brain stimulators, and neuroprosthetics for spinal cord injuries, require large-animal models like sheep and pigs. These animals are ideal for:
- Testing electrode placement and stimulation accuracy
- Evaluating the long-term safety of neuroprosthetic devices
- Assessing device integration and tissue response over time
These models are essential for ensuring that devices designed to treat neurological disorders are both effective and safe for long-term use.
2.4 Soft Tissue Repair and Implant Materials
Soft tissue repair materials, such as those used in hernia repairs, wound healing, or subcutaneous implants, are commonly tested in small to medium-sized animals like rats and rabbits. These models are used to assess:
- Tissue regeneration and healing after implantation of biomaterials
- Immune response to implanted devices
- The absorption or degradation rates of bioresorbable materials
For example, animal models are used to test wound healing dressings or soft tissue scaffolds to ensure that they facilitate effective tissue repair without causing significant adverse reactions.
2.5 Ophthalmic Devices
Ophthalmic devices, such as contact lenses, intraocular lenses (IOLs), or surgical devices for retinal treatments, require specialized models for testing. Rabbits, pigs, and dogs are commonly used to assess:
- The safety and performance of contact lenses or intraocular implants
- The interaction between the device and the ocular tissue
- Long-term effects on vision, including potential complications like infection or inflammation
Animal models are critical for testing ophthalmic devices due to the delicate nature of the eye and its intricate relationship with foreign materials.
2.6 Aesthetic and Dermatological Devices
In the medical aesthetics and dermatology fields, devices like laser systems, micro-needling devices, and dermal fillers are tested in animal models to ensure:
- Safety and efficacy of non-invasive procedures like skin rejuvenation
- Long-term effects of injectable dermal fillers on tissue regeneration and potential complications
- Performance of devices used in treatments such as hair removal or skin resurfacing
For instance, rabbit or pig models are often used to evaluate laser-based aesthetic devices, as these species have skin that closely resembles human skin, allowing researchers to assess skin response, healing, and overall safety.
Animal models are essential for understanding how devices function and perform under long-term use. Whether it’s assessing cardiovascular, orthopedic, soft tissue, or ophthalmic devices, these studies provide invaluable insights into device safety and performance in real-world conditions.
They help ensure that devices will perform safely and effectively over time, allowing manufacturers to refine their designs and meet medical device regulations before clinical trials.
Through rigorous animal testing, medical device manufacturers can confidently move forward in the development of safer and more effective devices for patients.
3. Meeting Global Regulatory Requirements
Understanding Medical Device Regulations
Global medical device regulations require manufacturers to conduct comprehensive animal studies. Regulatory agencies like the FDA, EMA, and NMPA have specific requirements for:
- Types of device testing (e.g., biocompatibility, efficacy, long-term safety)
- Preferred animal species for different device types
- Study duration and key endpoints (e.g., acute toxicity, long-term healing)
Compliance with these regulations is essential for successful evaluation of medical devices.
The Importance of GLP Compliance
Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) ensures that animal testing is conducted in a consistent, reliable, and scientifically sound manner. GLP-compliant studies improve the quality of data, making it more likely to be accepted by regulatory bodies for clinical trial approval. GLP compliance is also important because it:
- Guarantees that the data is reproducible and traceable
- Reduces the likelihood of delays or re-testing
- Supports the evaluation of medical devices with reliable, high-quality evidence
Designing Effective Animal Studies
Properly designed studies are essential for ensuring the validity and scientific rigor of the data. Key considerations include:
- Sample size: Ensure that enough animals are used to detect meaningful differences
- Control groups: Use appropriate controls to eliminate confounding variables
- Randomization and blinding: Reduce bias in data collection and analysis
- End points: Define clear success criteria linked to device performance
Well-designed studies result in reliable, reproducible data that will meet regulatory bodies' requirements.
4.Case Study: GLP Testing for a Biodegradable Stent
A company developing a biodegradable stent performed a GLP-compliant study using a large-animal model. The study demonstrated:
- Safe and predictable degradation of the stent over time
- No systemic toxicity or adverse effects
- Stable vessel healing and patency after implantation
This high-quality data played a key role in gaining FDA approval and allowed the device to move quickly into clinical trials.
Conclusion: A Critical Step in Medical Device Development
Animal testing remains an essential part of the evaluation of medical devices. It helps ensure that devices are safe, effective, and perform well over the long term.
Through device testing, manufacturers can meet medical device regulations, reduce risks, and ultimately protect patients. Well-designed animal studies are a critical part of any medical device development program and can accelerate the time to clinical trial approval.
The HuaTeng Biotechnology Approach – Plan Your Preclinical Testing with Us
If you are ready to begin your device testing program, we offer comprehensive testing services to help you navigate the regulatory landscape and design studies that meet all necessary requirements.
[Contact Us] to discuss how our team can support your project and ensure a successful evaluation of medical devices.